DPMO
Personalize This
Get insights for your role
DPMO (Defects Per Million Opportunities) is a Six Sigma metric that measures process quality by calculating defects relative to total opportunities.
Definition
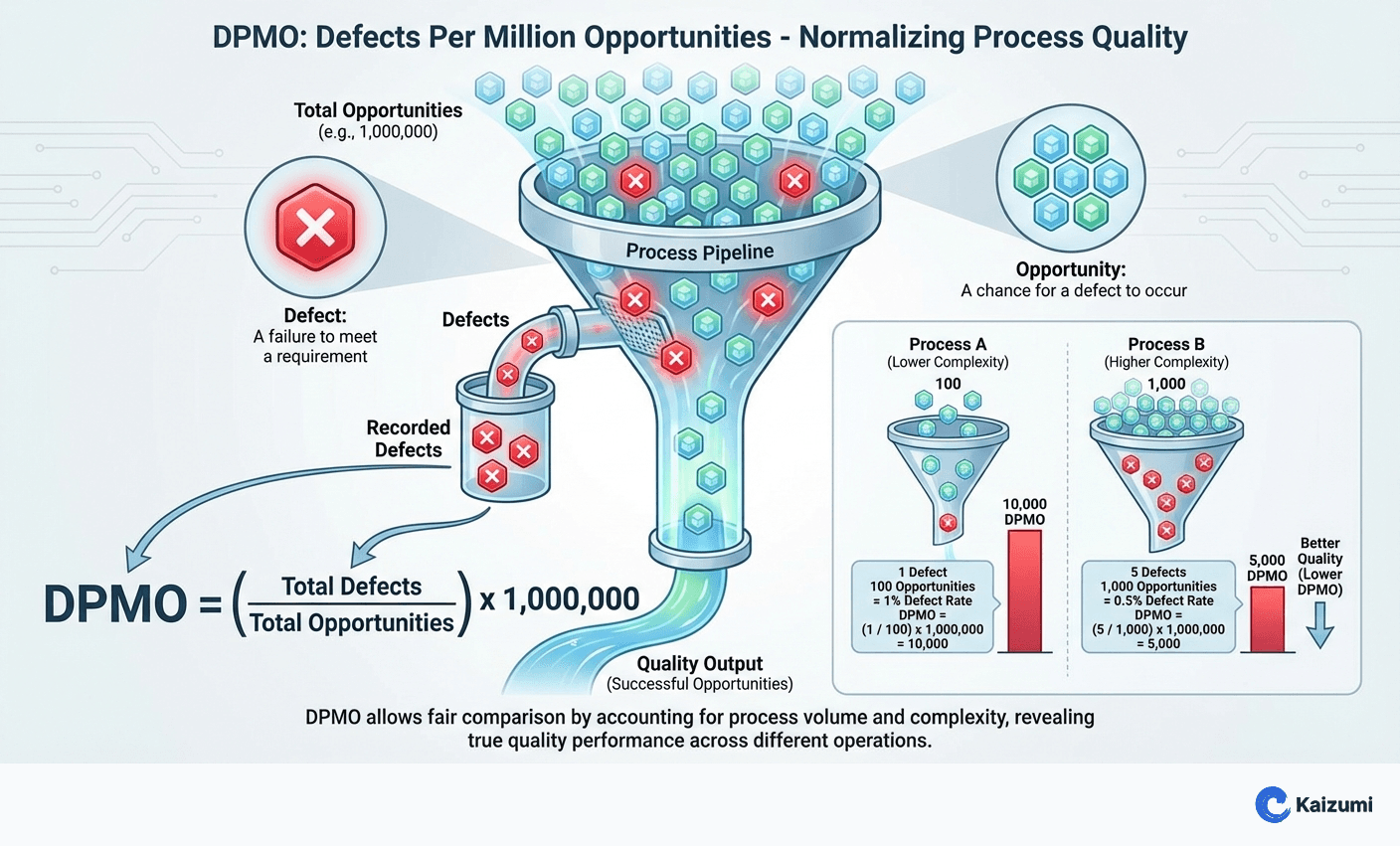
DPMO (Defects Per Million Opportunities) is a metric that expresses process quality by calculating the number of defects that would occur if the process produced one million opportunities. It normalizes quality measurement across different processes by accounting for complexity—a process with 10 opportunities for defect per unit is measured on the same scale as one with 100 opportunities. DPMO directly converts to sigma level, the core performance metric in Six Sigma methodology.
Examples
A circuit board has 500 solder joints (opportunities for defect). In 1,000 boards produced, inspectors found 25 defective joints. DPMO = (25 ÷ (1,000 × 500)) × 1,000,000 = 50 DPMO, equivalent to approximately 5.1 sigma—world-class quality.
Key Points
- Formula: DPMO = (Total Defects ÷ Total Opportunities) × 1,000,000
- Six Sigma target is 3.4 DPMO (99.99966% defect-free)
- Allows comparison across processes with different complexity levels
- Must clearly define what constitutes a "defect" and an "opportunity"
Common Misconceptions
Lower DPMO is always better regardless of cost. Moving from 1,000 DPMO to 100 DPMO might cost $10,000, but moving from 100 to 10 might cost $1 million. The business case must justify the improvement investment.
DPMO and defect rate are the same thing. Defect rate measures defective units; DPMO measures individual defect opportunities. A unit with 3 defects counts as one defective unit but three defect opportunities.