Statistical Process Control
Personalize This
Get insights for your role
Statistical Process Control (SPC) uses statistical methods to monitor and control processes, distinguishing normal variation from signals requiring action.
Definition
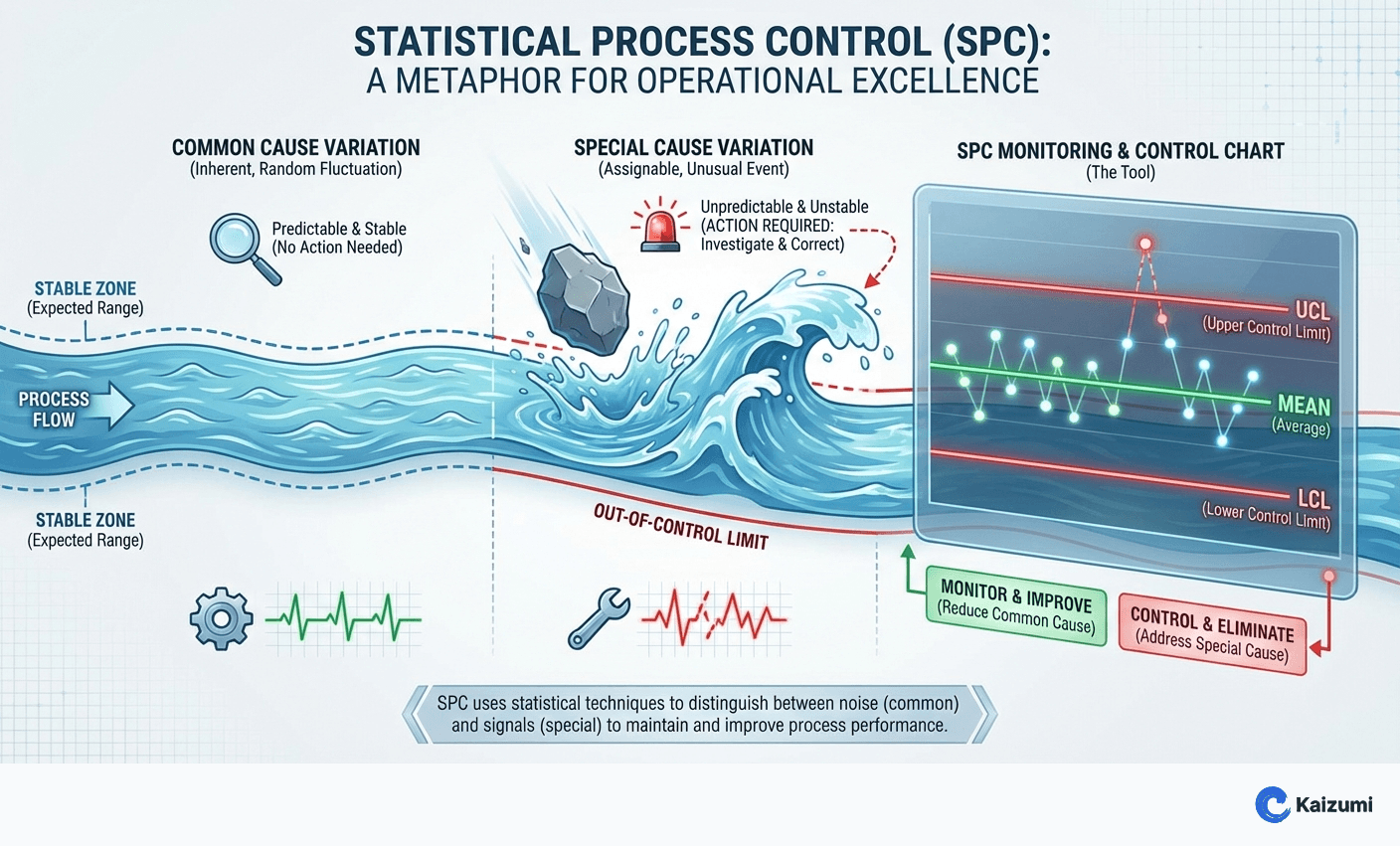
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a methodology that uses statistical techniques to monitor, control, and improve process performance. The core principle is distinguishing between common cause variation (inherent, random fluctuation) and special cause variation (assignable, unusual events). SPC uses control charts as its primary tool, enabling operators to detect process changes in real-time and take corrective action before defects occur. Developed by Walter Shewhart in the 1920s, SPC remains fundamental to quality management.
Examples
An injection molding operation monitors part weight using SPC. Operators check control charts every 30 minutes. When the chart signals a shift (seven consecutive points above the mean), they investigate and find a material batch with higher moisture content. Adjustment prevents a production run of defective parts.
Key Points
- Common cause variation is inherent to the process and requires system-level changes to reduce
- Special cause variation is assignable to specific events and requires local investigation
- Reacting to common cause as if it were special cause (over-adjustment) increases variation
- SPC enables proactive control rather than reactive inspection
Common Misconceptions
SPC means controlling to specifications. SPC controls to the process's natural behavior (control limits), not specifications. A process can be in statistical control while producing defects, or out of control while meeting specs. Both require different improvement approaches.
SPC requires sophisticated software. Basic SPC can be done with paper charts and calculators. While software helps with data collection and analysis, the fundamental concepts are simple. Understanding when to act versus when to leave alone is the key skill.