Balanced Scorecard
Personalize This
Get insights for your role
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework that measures performance across four perspectives: financial, customer, process, and learning.
Definition
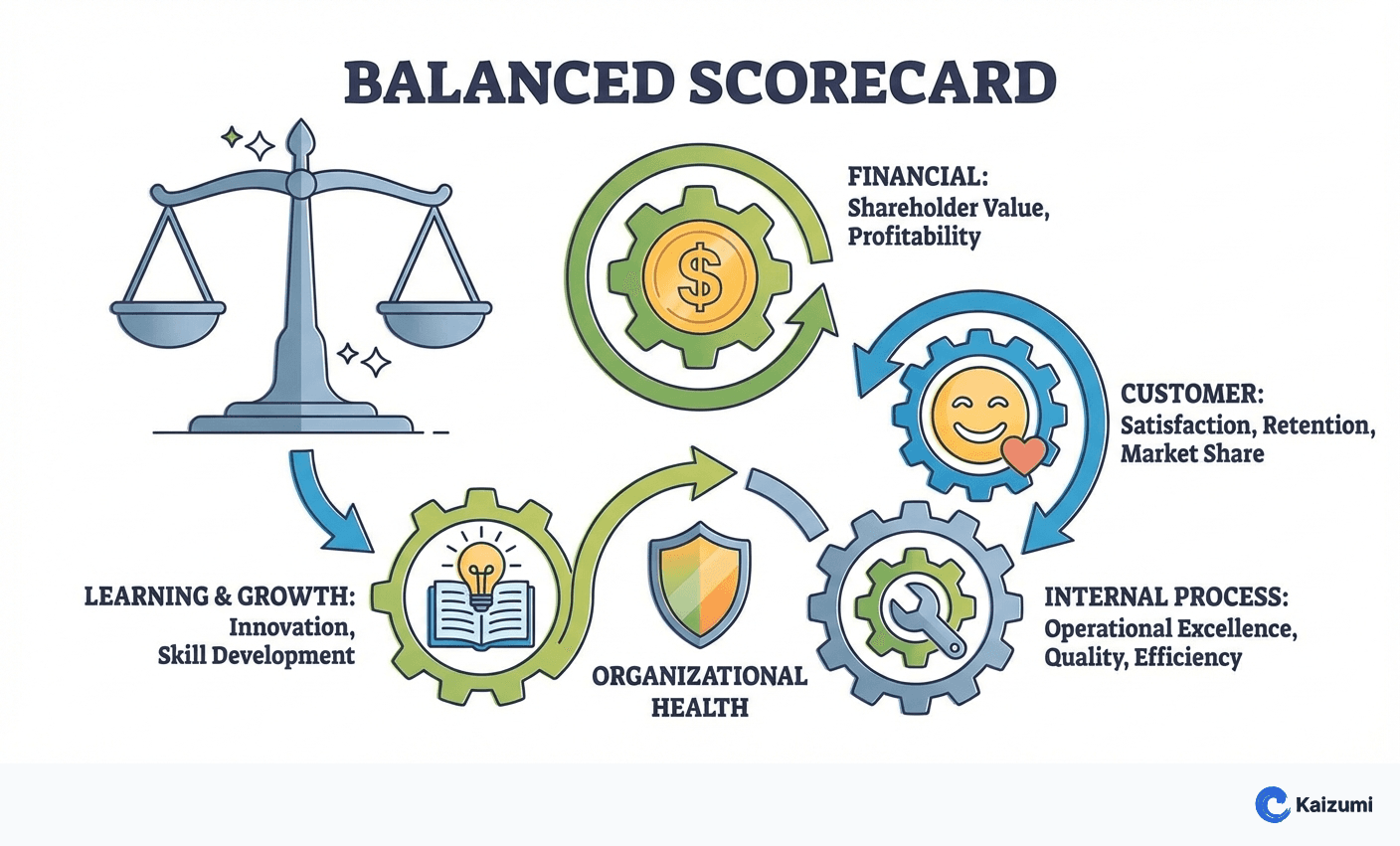
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management framework that measures organizational health across four interconnected perspectives: Financial (shareholder value, profitability), Customer (satisfaction, retention, market share), Internal Process (operational excellence, quality, efficiency), and Learning & Growth (employee capabilities, innovation, systems). By balancing measures across perspectives, organizations avoid optimizing one area at the expense of others and create cause-effect linkages showing how capabilities drive process performance, customer results, and ultimately financial outcomes.
Examples
A plant's balanced scorecard included: Financial (cost per unit, asset utilization), Customer (on-time delivery, quality complaints), Process (OEE, first-pass yield), Learning (training hours, skill certifications). Reviewing all perspectives prevented overemphasis on cost at the expense of quality or capability.
Key Points
- Four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Process, Learning & Growth
- Creates balance—avoids overoptimizing one area at expense of others
- Establishes cause-effect linkages between perspectives
- Links operational metrics to strategic objectives
Common Misconceptions
Balanced Scorecard is just a reporting tool. The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management system—translating strategy into measurable objectives and aligning organization around them. It's about strategy execution, not just measurement.
All four perspectives are equally important. While all perspectives must be balanced, they're causally linked. Learning enables process improvement, which drives customer results, which produces financial outcomes. Understanding these linkages is essential.