Greenfield
Personalize This
Get insights for your role
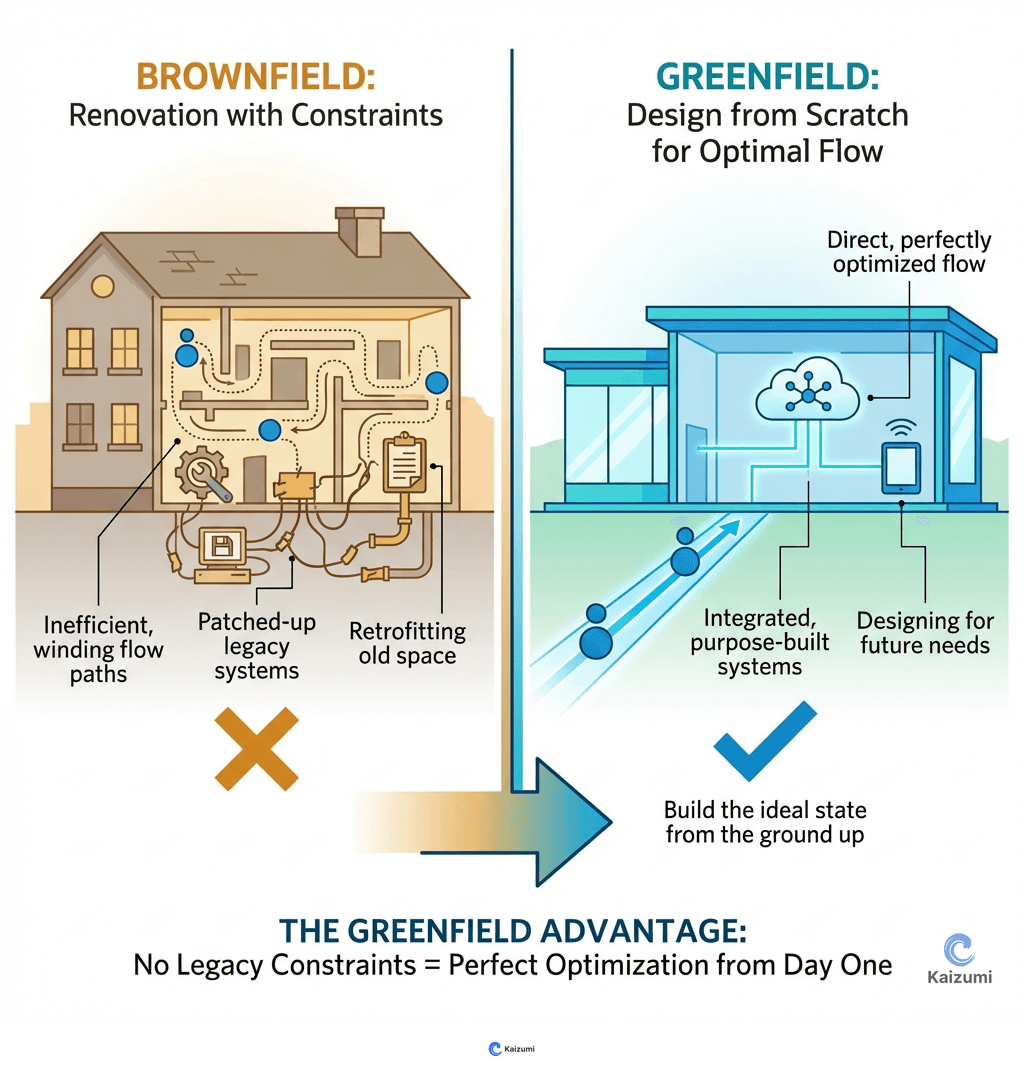
Greenfield refers to designing new operations from scratch with lean principles built in from the start, without legacy constraints.
Definition
Greenfield refers to designing and building new operations from the ground up with lean principles incorporated from the start. Without legacy equipment, existing layouts, or entrenched culture, greenfield provides the opportunity to design optimal flow, right-sized equipment, cellular layouts, and supporting management systems from day one. Greenfield is rare—most organizations work within existing constraints—but new plants, product lines, or major expansions offer greenfield opportunities. The 3P (Production Preparation Process) methodology is particularly valuable for greenfield design.
Examples
A company building a new plant on an empty site has a greenfield opportunity. They can design cellular layouts, size equipment for flow, plan for flexible staffing, and build visual management systems—things that would require major renovation in an existing plant.
Key Points
- Opportunity to design lean principles in, not retrofit them
- Relatively rare—most improvement happens in brownfield settings
- Requires discipline to actually design optimally, not just replicate existing approaches
- 3P methodology helps capitalize on greenfield opportunities
Common Misconceptions
Greenfield guarantees lean success. Without discipline, greenfield implementations often recreate traditional approaches because that's what people know. A clean slate is opportunity, not guarantee.
Greenfield is always better. Greenfield lacks existing expertise, supplier relationships, and proven processes. The constraint-free environment also means everything must be built from scratch.