Fixed-Position Stop System
Personalize This
Get insights for your role
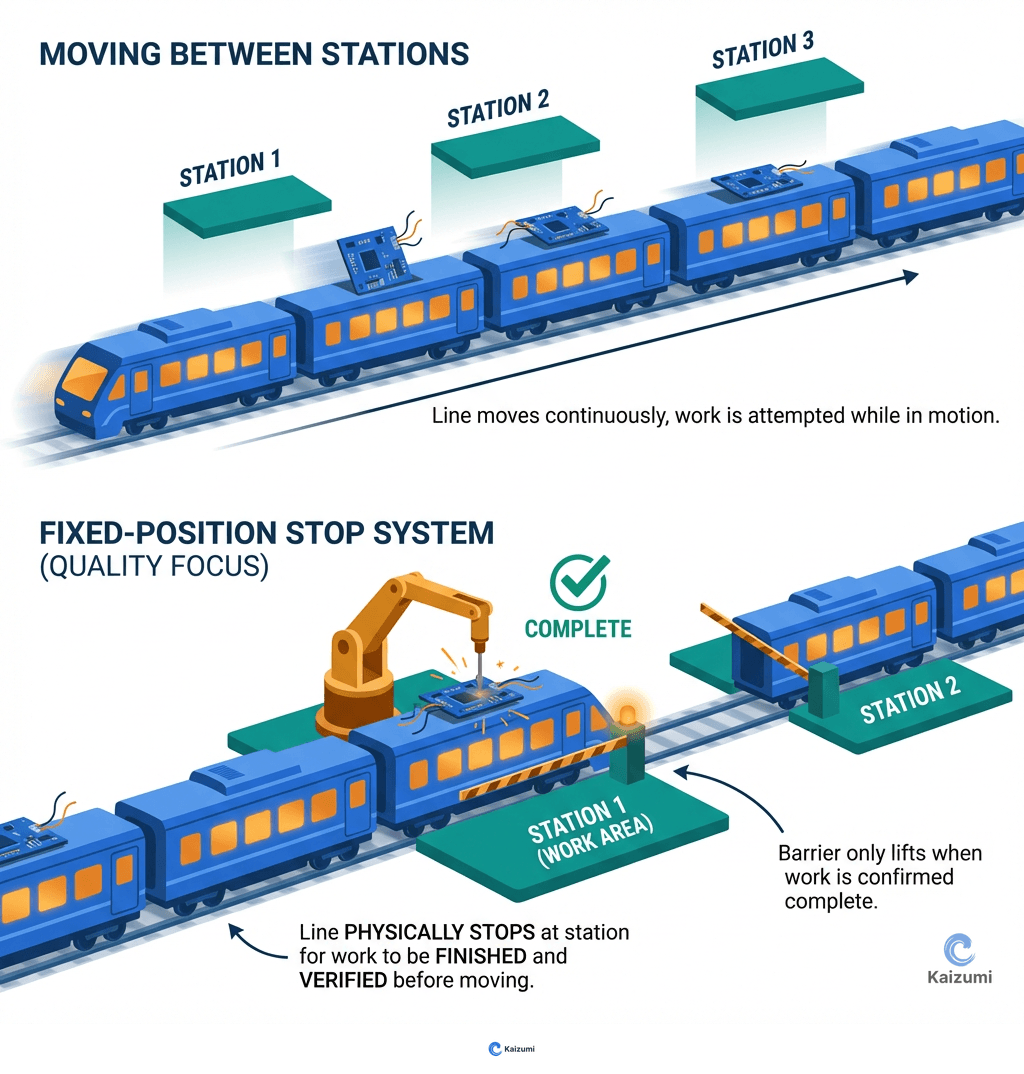
A fixed-position stop system halts a moving production line at predetermined points, ensuring problems are addressed at specific locations.
Definition
A fixed-position stop system is a line control method where a moving assembly line stops at predetermined positions rather than running continuously. The line advances one position at takt time intervals, then stops while operators complete their work. If an operator cannot complete their work within the takt interval, they pull the andon cord before the line advances. This allows the problem to be addressed at a known position with the product in a defined state. Unlike continuous-motion lines where problems result in incomplete work being passed downstream, fixed-position stops ensure work is either complete or the line waits.
Examples
An automotive assembly line advances every 60 seconds and stops for work. If an operator can't install a component before the next advance, they signal with the andon. The team leader has until the next stop position to resolve the issue—either helping complete the work or stopping the line for problem-solving. Every car reaches the end with all work complete.
Key Points
- Lines stop at the same positions every cycle, making problem locations predictable
- Operators have the full takt interval to complete work, with clear visual indication of progress
- Problems surface at specific locations where root causes can be identified
- Requires line design with defined stop positions and advance mechanisms
Common Misconceptions
Fixed-position stops reduce efficiency. The brief stops are negligible compared to the cost of downstream defects. Continuous-motion lines often appear faster but produce more rework and quality escapes.
Any line can use fixed-position stops. Lines must be designed for discrete advances. Continuous processes (conveyors with no position control) require different quality control approaches.